Corporate Practice of Medicine and Management Service Organizations
In many states, a legal principle known as the prohibition on the Corporate Practice of Medicine (CPOM) restricts the ownership of medical practices, including medical spas and IV hydration businesses, to licensed physicians. For non-physicians—such as entrepreneurs, investors, and non-physician clinical personnel—interested in entering the medical spa or IV hydration industry, a Management Service Organization (MSO) can provide a viable solution for participating in an otherwise restricted field.
What is the Corporate Practice of Medicine (CPOM)?
The CPOM doctrine is designed to encourage ethical medical practices and ensure that patient care remains the top priority. By restricting the practice ownership of medicine to licensed physicians, the CPOM helps to prevent non-medical entities from making clinical decisions that could compromise patient safety and care quality.
Essentially, Corporate Practice of Medicine laws mean that only doctors can own medical businesses. However, if you are not a doctor but wish to invest in or manage the administrative side of a medical spa or IV hydration business, you can do so through an MSO. This structure allows non-doctors to participate in the business side of healthcare without breaking the law.
What is an MSO?
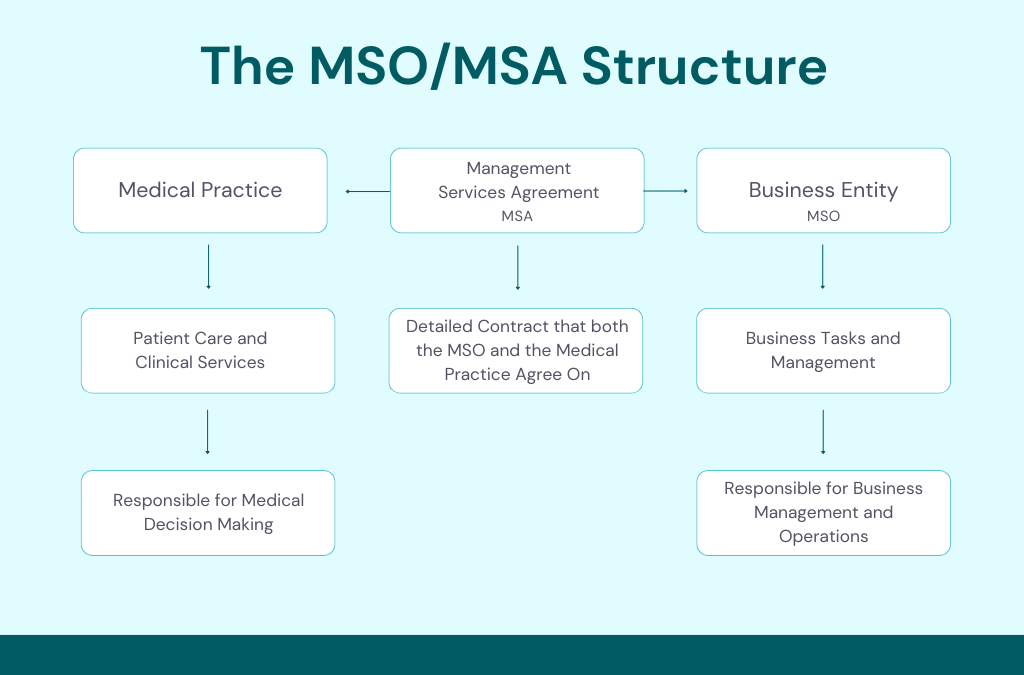
An MSO is a business entity that provides management and administrative services to a medical practice. These services can include billing and collections, marketing, office space management, and accounting, among other things. The MSO can also own the medical spa’s brand name and logo, licensing these to the medical practice.
Under the MSO model, the medical practice retains control over clinical decision-making and patient care, while the MSO handles the business operations. This separation allows physicians to concentrate on clinical activities without being bogged down by administrative tasks. In exchange for its services, the medical practice pays the MSO a fee. The details of the services provided and the fees charged are outlined in a Management Services Agreement (MSA).
To put it simply, an MSO is like a support system for medical practices. It takes care of the business side of things so that doctors and healthcare providers can focus on patient care. This can be very helpful, since running a medical practice involves a lot of administrative tasks that can be time-consuming and complex. By having an MSO handle these tasks, healthcare providers can ensure that their practice runs smoothly and efficiently while focusing on quality patient care.
What is an MSA?
In order for an MSO and medical practice to formalize their relationship, as well as clearly outline the expectations, responsibilities, and services provided between the two entities, they will enter into a Management Services Agreement (“MSA”).
An MSA is a binding legal contract between an MSO and a medical practice that governs the relationship between the two parties, including specifying what services the MSO will provide to the medical practice, outlining how the MSO will be paid for those services, and determining how disputes between the parties will be resolved. The MSA will also clearly designate what services will not be provided by the MSO–namely, any and all clinical services.
Think of an MSA as a detailed plan that both the MSO and the medical practice agree on. It spells out exactly what the MSO will do and how much they will be paid for their services. It also makes it clear that the MSO is only responsible for administrative and business tasks, not for making any medical decisions. This helps to prevent any misunderstandings and ensures that both parties know what to expect from the arrangement.
How Much Does a Medical Director Typically Get Paid in an MSO/MSA?
The current market rate is about $500-$2,000 a month for a start-up practice.
Navigating Exceptions to the CPOM
There are certain statutory exceptions to the CPOM, allowing for specific relationships between physicians and non-physicians. These exceptions include physician employment by non-profits, certain rural hospitals, and other specified entities as well as certain shared ownership allowances between certain healthcare providers. It is crucial for any business or medical professional entering into such arrangements to ensure they meet all statutory requirements to remain compliant with the law. Violations of the CPOM can lead to severe penalties, including fines and suspension of medical licenses by the Medical Board.
How Can Lengea Law Help?
To navigate the complexities of CPOM and ensure compliance with relevant healthcare laws, it is essential to seek proactive legal guidance. Lengea Law offers expert advice on business transactions, contracts, and regulatory issues to prevent violations and protect your practice from legal challenges.
Our experienced team provides comprehensive regulatory counsel and business advice for clients entering the medical spa industry. We assist with MSO/MSA processes, including entity formation and drafting legal documents. Contact us today to start your journey into the medical spa sector with confidence.